CHAPTER 3 - VOLCANIC ROCKS (P. 49-68)
MAGMA - molten rock and dissolved gas (in the subsurface).
LAVA - magma that reaches the Earth's surface before cooling (most gasses have
escaped).
Magma is like seltzer: It contains "Volatile gases" - H20, CO2, SO2, N2, CH4 and
other dissolved gases.
TWO GENERAL CLASSES OF IGNEOUS FEATURES
- EXTRUSIVE or VOLCANIC (surface)
- INTRUSIVE or PLUTONIC (subsurface)
CRYSTALLIZATION - the formation and growth of a crystalline solid from a liquid or
a gas; crystals are the orderly arrangement of atoms in a framework. In IGNEOUS
ROCKS, crystal size is a reflection of:
- slow cooling: large crystals (deep underground)
- fast cooling: small crystals (near surface)
- very rapid cooling: glass (without Volatile compounds like CO2, H2O)
in a confined space, such as IN lava or magma, crystals are interlocking. The
crystals we see in museums typically grew on the walls of underground caverns or
empty spaces left by fluids (water or gas) in the earth.
IGNEOUS ROCK TEXTURES
The term texture applies to the overall appearance of the rock based on
the size and arrangement of the interlocking crystals. Textural terms include:
- APHANITIC TEXTURE - Igneous rocks that form on the earth's surface have
very fine-grained texture because the crystals are too small to see without
magnification.
- PHANERITIC TEXTURE - Igneous rocks with large, visible crystals because the
rock formed slowly in an underground magma chamber.
- PORPHYRITIC TEXTURE - an igneous rock in which PHENOCRYSTS (large
crystals) are surrounded by a fine groundmass (very small crystals). This shows
that the large crystals had a chance to form in a magma while it was migrating and
cooling.
- GLASSY TEXTURE (caused by rapid cooling); fresh fractures display a
conchoidal fracture like broken glass. An igneous rock with glassy texture is called
OBSIDIAN.
- PYROCLASTIC TEXTURE - igneous rock formed from consolidated fragments
of cooling magma blown out of a volcano comes in various shapes: BLOCKS
(chunks of rock), BOMBS (molten blobs), CINDERS, and fine ASH. These materials
may be "welded" together by heat, or cemented together by other processes later.
CINDERS have lots of VESICLES (holes created by escaping gases at the lava
cools). PUMICE is a type of glassy cinder that has so much gas trapped in the rock
that it will float on water.
MINERAL COMPOSITION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
BOWEN'S REACTION SERIES explains how the composition of magma changes at
it cools. HIGH TEMPERATURE (Mafic) MINERALS form first and SETTLE OUT (by
sinking to the bottom of the magma chamber). As the magma continues to cool all
the high temperature minerals form first, leaving a cooler, but still molten rock
(magma). As this magma cools to form rock the last minerals to crystallize are the
LOW TEMPERATURE (Felsic) MINERALS. This process changes the composition of
the magma as it cools: this process is called MAGMATIC DIFFERENTIATION.
The MANTLE (which is ultimately the source of heat rising in the earth's CRUST) is
nearly homogeneous in composition, Consists of an ULTRAMAFIC rock called
PERIDOTITE composed of the minerals OLIVENE, PYROXENE, PLAGIOCLASE (Ca-
Feldspar), plus other minerals and dissolved gases.
MAFIC ROCKS
Where magma from the MANTLE reaches the surface, such as along mid-ocean
ridges and large, hot, igneous plumes rising under certain volcanos, like HAWAII,
the composition of the lava has not changed very much. The magma is very
MAFIC in composition. MAFIC IGNEOUS ROCKS include:
- GABBRO - phaneritic (large crystals) of mafic minerals: olivine, pyroxene, etc.
- BASALT - aphanitic (small crystals) of mafic minerals: olivene, pyroxene, etc.
Mafic rocks (basalt and gabbro) are very dark in color, and very dense because of
their high iron content. Mafic rocks are abundant in the earth's crust beneath the
oceans.
FELSIC ROCKS
Magma that has undergone a high degree of MAGMATIC DIFFERENTIATION has a
composition consisting of FELSIC MINERALS (low temperature igneous minerals,
such as quarts, K-spar, Na-spar, and mica. Felsic rocks include:
- GRANITE - phaneritic rock (consisting of large crystals of K-spar, Quartz, Na-
spar, and Mica) - usually pink to white, most common in continental crustal rocks
(examples of places were granite is abundant on the earth's surface: Rocky
Mountains, Appalachian, Canadian Shield region.
- RHYOLITE - aphanitic (small crystals) of felsic minerals with the same
composition of granite.
ANDESITIC ROCKS
ANDESITE is a medium gray, fine grained rock of volcanic origin, named after the
Andes Mountain, but is abundant in all volcanic regions associated with subduction
zones (where crust is sinking and partially remelting - example: volcanos associated
with the Pacific "Ring of Fire"). Andesite is INTERMEDIATE in composition
between MAFIC and FELSIC rocks. The mixture of mafic and felsic minerals gives
the rock a "salt and pepper" appearance.
- DIORITE - phaneritic rock (large crystals) of both mafic and felsic minerals.
- ANDESITE - aphanitic rock (small crystals) of both mafic and felsic minerals.
SUMMARY:
Intrusive: Gabbro Diorite Granite
Extrusive: Basalt Andesite Rhyolite
SUBSURFACE (INTRUSIVE) IGNEOUS FEATURES
HYDROTHERMAL SOLUTIONS - "volatilize gases" that escape from magma
(water, CO2, Methane) plus "dissolved" minerals.
HYDROTHERMAL DEPOSITS - precipitates from solutions escaping from a magma
chamber, form VEIN DEPOSITS. Often form economic deposits of gold, copper,
zinc, silver, and other metals.
PEGMATITE - very large crystals of igneous minerals form near the top of a gas
saturated igneous intrusion.
FEATURES ASSOCIATED WITH INTRUSIVE IGNEOUS ACTIVITY
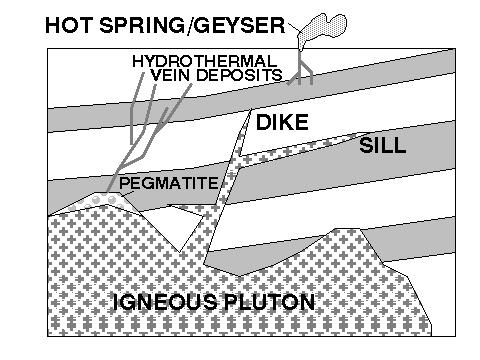
NOTE: The PALISADES, a long rocky cliff in NJ along the western side of the
Hudson River in the vicinity of the George Washington Bridge is an excellent
example of a SILL, a large volcanic intrusion that squeezed in between sedimentary
rock layers that were at one time buried deep beneath the earth's surface.
 Click here to
return to the Class Website
Click here to
return to the Class Website

 Click here to
return to the Class Website
Click here to
return to the Class Website