Understanding
map units and display units
Map units
are the units in which the coordinates for a dataset are stored. They are
determined by the coordinate system. If the data is stored in a geographic
coordinate system, the map units are usually decimal degrees (degrees, minutes,
and seconds expressed as a decimal). If the data is stored in a projected
coordinate system, the map units are usually meters or feet. Map units can be
changed only by changing the data's coordinate system.
Display
units are independent of map units—they are a property of a data frame. Display
units are the units in which ArcMap displays coordinate values and reports
measurements. You can set the display units for any data frame and change them
at any time.
![]() More about decimal degrees
More about decimal degrees
Recall that latitude and longitude coordinate values are
actually angle measurements. Angles are measured in degrees. For
latitude-longitude coordinates, degrees can be expressed two ways: as degrees,
minutes, seconds (DMS) or as decimal degrees (DD). In a
Below is an example of how to convert a coordinate location
from DMS to DD.
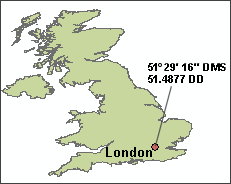
The latitude of
1. Divide each value by the number of
minutes (60) or seconds (3600) in a degree:
29 minutes = 29/60 = 0.4833 degrees
16 seconds = 16/3600 = 0.0044 degrees
2. Add up the degrees to get the
answer:
51° + 0.4833 ° + 0.0044 ° = 51.4877 DD