Geographic
coordinate systems
A
geographic coordinate system is a reference system for identifying locations
and measuring features on the curved surface of the earth. It consists of a
network of intersecting lines called a graticule. The intersecting lines of the
graticule are probably familiar terms to you—longitude and latitude.
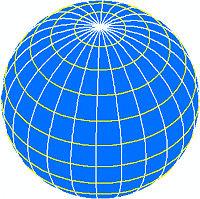
The graticule is made up of
vertical lines, called lines of longitude, and horizontal lines, called lines
of latitude. Because the earth is spherical, these lines form circles.
In a
geographic coordinate system, measurements are expressed in degrees, minutes,
and seconds. A degree is 1/360th of a circle. Each degree can be divided into
60 minutes, and each minute can be divided into 60 seconds.
Lines of longitude
are called meridians. Measures of longitude begin at the prime meridian (which
defines the zero value for longitude) and range from 0° to 180° going east and
from 0° to -180° going west.
Lines of
latitude are called parallels. Measures of latitude begin at the equator and
range from 0° to 90° from the equator to the north pole
and from 0° to -90° from the equator to the south pole.
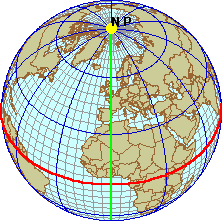
The prime meridian (green line) is
the starting point for longitude and has a value of 0. The equator (red line)
is the starting point for latitude and has a value of 0. It runs midway between
the north and south poles, dividing the earth into northern and southern
hemispheres.
![]() More about prime meridians
More about prime meridians
Choosing which meridian will be the prime meridian is
completely arbitrary. For example, the Spanish have used a meridian passing
through
Later, the
Longitude
and latitude are actually angles measured from the earth's center to a point on
the earth's surface. For example, consider the location referenced by the
following coordinates:
Longitude: 60 degrees East (60° 00' 00")
Latitude: 55 degrees, 30 minutes North (55° 30' 00")
The
longitude coordinate refers to the angle formed by two lines, one at the prime
meridian and the other extending east along the equator. The latitude
coordinate refers to the angle formed by two lines, one on the equator and the
other extending north along the 60° meridian.
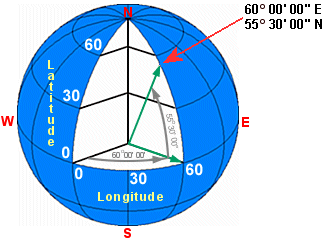
Longitude and latitude are angles
measured from the earth's center to a point on the earth's surface.