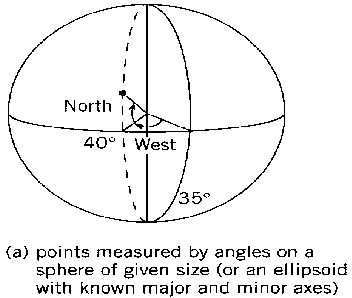
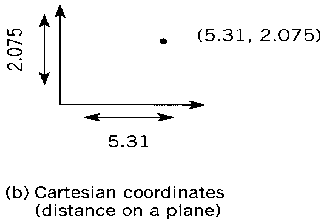
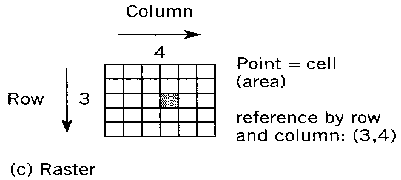



Coordinate reference systems: Measurements relative to a spatial reference system.(a) Spherical coordinates measure angles on a solid surface of a given radius. This system can also handle location on an ellipsoid (a distorted sphere); (b) Cartesian coordinates based on distances along two axes. Note that the convention of (X,Y) is somewhat arbitrary; some Cartesian coordinates such as UTM were given as (northing, easting); (c) Cellular coordinates counted as integers. Raster hardware tends to sweep from the top of screen to the bottom, so the convention is more likely to place Row 1 at the "top" or north of an image.